n ®RMe
Rme= 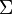
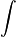
i [M+C +m / d2/ c = e]
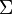
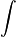
I = 1
Matéria, campo, movimento / distância
ao quadrado / velocidade da luz = energia.
Isto vemos na produção de
eletricidade onde a eletricidade sempre está ligada a matéria, ao magnetismo e
ao movimento, ou seja, não se tem eletricidade sem movimento. E isto varia
conforme a distância entre matéria e magnetismo e o movimento em que eles se
encontram.
Isto vemos também na produção de
energia atômica e fissão nuclear.
Vemos isto também em relação a
inércia da gravidade, onde temos um inércia vertical, e que um avião tende a
romper esta inércia se transforma em inércia do movimento e horizontal onde
rompe com a inércia da gravidade. Se transformando em energia inercial
horizontal e do movimento.
O crescimento da inércia.
A inercia aumenta proporcionalmente
conforme aumenta a velocidade.
Ou seja, se temos um foguete em
grande aceleração descendo em direção ao planeta. Temos que levar em
consideração a inercia da força da gravidade e a inercia da velocidade, e que
pode ser proporcional a um crescimento de progressão geométrica conforme
aumenta a aceleração.
Vemos isto também na energia da
dilação e oscilação de gases e moléculas, e elétrons que tem o seu potencial de
energia conforme se aumenta o movimento conforme se aumenta a temperatura e
dilatação.
O nêutron Graceli estabilizador de
cargas positivas e negativas.
O nêutron não é uma partícula sem
cargas positiva ou negativa, mas sim é uma partícula com as duas cargas que tem
a função de estabilizar o sistema dentro do átomo, ou seja, atua sobre as
cargas positiva e negativa absorvendo e diminuindo a sua função com suas
próprias cargas negativa e positiva.
Quando se tem um sistema de muitos
elétrons com ações de cargas negativas o nêutron entra em cena agindo e
estabilizando a radiação interna do átomo.
O mesmo quando temos um sistema de
muitos pósitrons e prótons agindo o sistema interno e diminuindo o fluxo de
radiação para fora do átomo , mantendo todo sistema em questão num fluxo
radioativo mínimo e ínfimo.
Na verdade o nêutron deveria ser
chamado de estabilizador e não de nêutron. E é o estabilisador das forcas
dentro dos átomos e molécula, e o direcionamento desta estabilidade que produz
a energia nuclear e produz os elementos químicos e as suas famílias.
Temos assim, a geometria Graceli
nuclear quântica [gGnq] que varia em relação a energia nuclear magnética [enm],
interações [i], campos e cargas [cc], e fluxos com impulsos alternados ínfimos
de [ondas logiΦ /iΦ
/iΦ [n..]].
[n..]].
 /iΦ
/iΦ [n..]].
[n..]].
n ® gGnq
gGnq = 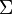
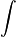
i [enm*h + cc = i = logiΦ /iΦ
/iΦ [a,Φ
[a,Φ ,0[n..]
,0[n..]
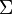
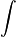
 /iΦ
/iΦ [a,Φ
[a,Φ ,0[n..]
,0[n..]
I = 1
Por isto que o nêutron tem o momento,
a energia magnética e uma geometria quântica ondular em torno dele mesmo e em
torno dos átomos.
Graceli relativism.
n ®RMe
Rme= 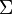
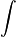
i [M+C +m / d2/ c = e]
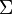
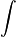
I = 1
Matter field, motion / distance squared / speed of light = energy.
This we see in the production of electricity where the electricity is always on the matter, magnetism and motion, ie, does not have electricity without moving. And this varies according to the distance between matter and magnetism and the movement in which they meet.
This will also see the production of atomic energy and nuclear fission.
We see that also for the inertia of gravity, inertia which have a vertical and a plane tends to break this inertia becomes inertia and horizontal movement which breaks the inertia of gravity. Becoming horizontal inertial energy and movement.
The growth of inertia.
The inertia increases proportionally as speed increases.
That is, if we have a rocket in great acceleration down towards the planet. We must take into account the inertia of the force of gravity and the inertia of speed, and that may be proportional to an increase of geometric progression with increasing acceleration.
Also see that the delay and oscillation energy and gas molecules, and electrons that have potential as the movement energy increases as the temperature and dilation increases.
Graceli The neutron surge of positive and negative charges.
The neutron is a particle not without positive or negative charges but is a particle having two loads which has the function of stabilizing the system within the atom, that is, loads acting on the positive and negative absorbing and reducing its function its own positive and negative charges.
When you have a system with many electrons actions of negative charges the neutron enters the scene acting and stabilizing the internal radiation of the atom.
The same when we have a system of many positrons and protons acting internal system and decreasing the flow of radiation out of the atom, keeping the whole system in question a minimum and tiny radioactive flow.
Actually the neutron should be called stabilizer and no neutron. E is the stabilizer of the forces within the atom and molecule, and the direction of this stability that produces nuclear energy and produces the chemical elements and their families.
We thus nuclear Graceli geometry quantum [gGnq] which varies in relation to nuclear magnetic [ENM] interactions [i], and fillers fields [cc] and flows with insignificant alternating pulses [logiΦ waves / iΦ
waves / iΦ [n. .]].
[n. .]].
 waves / iΦ
waves / iΦ [n. .]].
[n. .]].
n ® gGnq
gGnq = 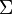
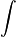
i [enm*h + cc = i = logiΦ /iΦ
/iΦ [a,Φ
[a,Φ ,0][n..]
,0][n..]
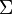
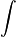
 /iΦ
/iΦ [a,Φ
[a,Φ ,0][n..]
,0][n..]
I = 1
For that the neutron has the time, magnetic energy and a quantum geometry curl himself around and around atoms.
Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário